Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by elevated levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. Glucose is a crucial source of energy for the body’s cells, and its levels are typically regulated by the hormone insulin, which is produced by the pancreas. Diabetes occurs when there are problems with insulin production or the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, leading to imbalanced blood sugar levels.
There are several types of diabetes, but the most common ones are:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body cannot produce insulin, and individuals with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to regulate their blood sugar levels. This form of diabetes typically develops in childhood or adolescence, and its exact cause is not fully understood.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, and in some cases, reduced insulin production over time. It is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and an unhealthy diet. Type 2 diabetes is more common in adults but can also occur in children and adolescents. It can often be managed through lifestyle modifications, medication, and, in some cases, insulin therapy.
- Gestational Diabetes: Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when blood sugar levels rise higher than normal. It usually resolves after childbirth, but women who have had gestational diabetes have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
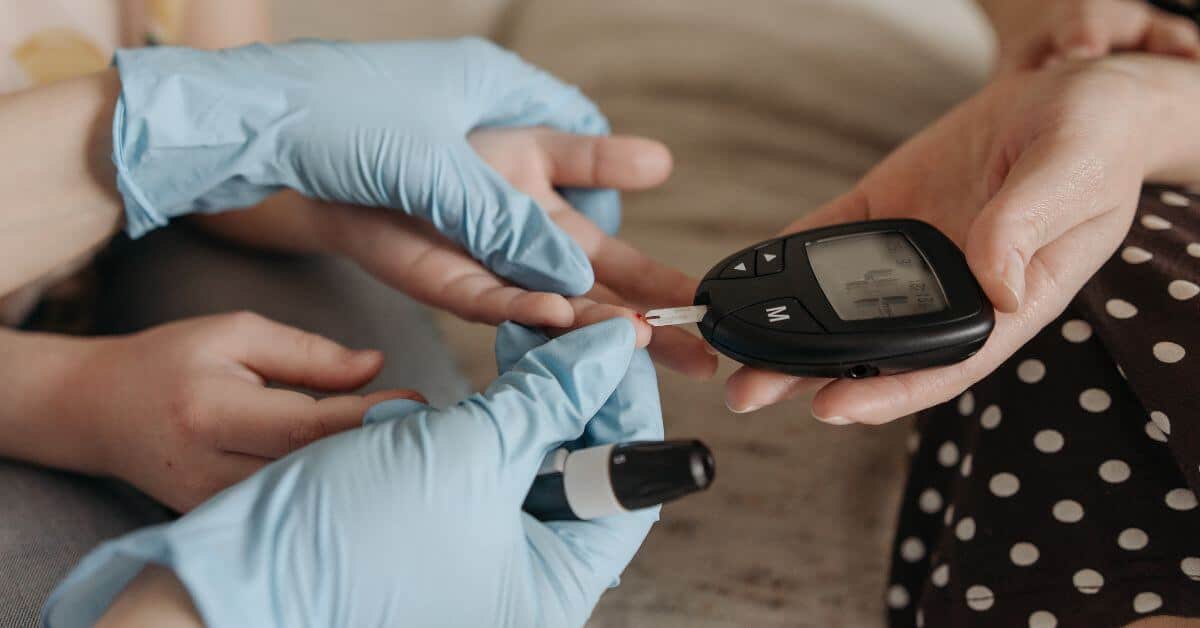
Common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision. However, some individuals with diabetes may not experience noticeable symptoms, especially in the early stages, which is why regular blood sugar testing is essential for diagnosis.
Managing diabetes involves controlling blood sugar levels within a target range to prevent or minimize complications. Treatment may include dietary modifications, regular physical activity, medication (such as oral medications or insulin), blood sugar monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments.
Diabetes is a serious condition that, if left uncontrolled, can lead to various health complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, eye problems, and foot complications. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals with diabetes to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive management plan tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
11 Healthy ways to avoid diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is largely influenced by lifestyle factors, and there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing this form of diabetes. Here are some key strategies to help you avoid diabetes:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
One of the most significant risk factors for type 2 diabetes is being overweight or obese. Losing excess weight, if you are overweight, can greatly reduce your risk. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% of your body weight can have a positive impact.
2. Adopt a Balanced Diet
Focus on a diet that is rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins (such as poultry, fish, and legumes), and healthy fats (like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil). Limit your intake of sugary beverages, processed foods, and high-sugar snacks.
3. Control Portion Sizes
Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating, which can lead to weight gain and imbalanced blood sugar levels.
4. Choose Complex Carbohydrates
Opt for complex carbohydrates like whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat) over refined carbohydrates (white bread, sugary cereals, white rice). Complex carbohydrates are digested more slowly and have a smaller impact on blood sugar levels.
5. Limit Sugar and Sugary Foods
Reduce your consumption of sugary beverages, sweets, and processed foods that contain added sugars. Read food labels to identify hidden sources of sugar in packaged products.
6. Stay Physically Active
Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and can lower your risk of type 2 diabetes. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training exercises at least two days a week.
7. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption. Smoking is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and excessive alcohol intake can affect blood sugar levels.
8. Get Regular Checkups
Visit your healthcare provider for regular checkups, and discuss your diabetes risk factors. They can perform blood sugar tests and provide guidance on managing your risk.
9. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can contribute to unhealthy eating habits and weight gain. Practice stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
10. Get Adequate Sleep
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Poor sleep can affect blood sugar regulation and increase the risk of diabetes.
11. Stay Informed
Educate yourself about diabetes risk factors and prevention strategies. Knowledge is a powerful tool for making informed choices.
It’s important to note that while these lifestyle changes can significantly reduce your risk of type 2 diabetes, they may not eliminate the risk entirely, especially if you have other risk factors like a family history of diabetes. Regular checkups with a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your health and catching any potential issues early.
If you have concerns about your diabetes risk or need personalized guidance on prevention, consider consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian who can provide tailored recommendations based on your individual circumstances.
# 7 Best Health & Fitness Apps: Digital Wellness Revolution
The Conclusion
In conclusion, while there is no known cure for diabetes, type 2 diabetes, in particular, can often be prevented or its risk significantly reduced through lifestyle modifications. Maintaining a healthy weight, adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and making other healthy choices can go a long way in reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Additionally, staying informed about diabetes risk factors and seeking regular healthcare checkups are important steps in managing and preventing the condition.
It’s crucial to remember that individual circumstances and genetics can play a role in diabetes risk, so what works best for one person may differ from another. Personalized guidance from healthcare professionals can help you make informed decisions and create a plan that suits your specific needs and circumstances. Overall, a proactive approach to a healthy lifestyle is the key to reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and promoting overall well-being.



[…] Properties: The seeds of Indian blackberry contain jamboline and jambosine, which help regulate blood sugar levels by increasing insulin activity and […]
[…] # 11 Healthy Ways to Avoid Diabetes: Blood Sugar Control […]